Power: An integral part of the Data Center
Publisher: Psychz Networks, July 19,2018
Electricity, commonly known as Power was discovered more a decade ago and since then it has become one of the most important sources behind any modern development. Today it has become an integral part of our century without which we can barely imagine progress.
But, surprisingly, it gets the least credit when we talk about in the computing domain. Without power we wouldn't be able to use those high capacities, lighting fast CPUs and arrays of storage stacked behind them. They would be all useless without electricity.
- About Data Centers
- Power Supply
- Generators
- Automated Transfer Switches (ATS)
- Uninterupted Power Supply (UPS)
- Cooling Units
- Power Distribution Units (PDU)
- Equipments
In the following article, we will discuss the importance of Power and how it is sourced and distributed in a fully equipped Data Center.
What are Data Centers?
A data center is a facility housing many networked computers that work together to process, store, and share data. With the help of Data Center, we can improve usability and reduce costs related to storage, bandwidth, and other networking components.
Data centers consume vast amounts of energy every year. Size for size they consume around 100 times the power used to run the average office building.
Rows of servers storing trillions of megabytes of information operate around the clock to enable organizations to run applications, process information and automate their operations. At home they allow you to upload a video, play a game, share a photo, e-mail a friend, tweet your location or check your bank balance.
Let us see how the power is distributed across a Data Center to run the infrastructure.
The supply of power at a bigger data center starts with the source which is connected to the main grid, which could be provided by the power supply company. In some of the Tier 4 Data Centers, there are usually two local companies supplying the power to reduce the risk of downtime should one sector fail.
In addition, In case of any major power outage, data centers are typically connected to at least one diesel or gas backup generator. Most data centers store enough fuel to keep the generator running for 24–48 hours.
This outline of a common data center power infrastructure roughly explains how modern data centers are able to supply
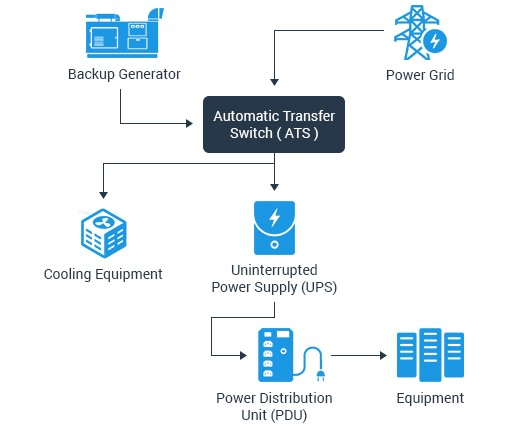
Let us go through each of the components that are labeled in the above distribution diagram
Power supply
The main power supply is sourced through local/national power supplying company. The 480V-208V distribution design is the most common and highly efficient. The overall efficiency, depending on the load, ranges, between 80%-85%, a significant improvement over the legacy computer room design. The power that is usually supplied by the power companies is Alternate Current.
There are two types of Current viz. Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC).
AC current is widely used across the world and it operates between 120 to 240 volts. The reason why it is widely used is that it can be transformed into different voltages quite easily.
Direct Current (DC) on the other hand is harder to measure. It is largely used in batteries.
The incoming power is a low-voltage electricity which then passes through an Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS) system, which provides short-term power when the input power source fails and protects critical components against voltage spikes, harmonic distortion, and other common power problems.
Most UPS systems are designed to provide power for at least 5 minutes on maximum load during an outage. These 5 minutes are good enough for the backup generators to start and take over the load from the UPS system.
Generators
Data Centre Generators provide a cost effective and reliable form of onsite power generation in case of a mainline outage. They can be configured in a similar way to UPS systems using either N, N+1, 2N and 2N+1 redundancy.
There are a number of Data Center generators available for back up. The main difference between these systems is the type of fuel they are able to use. Diesel, Bio-Diesel and Natural Gas have different advantages and disadvantages depending on your needs and environment.
Automated Transfer Switch (ATS)
Automated Transfer Switch (ATS) which are basically panels that house fuses, circuit breakers, and ground leakage protection units, take the low-voltage electricity and distribute it to Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS) system and other external entities like the cooling units. Automated Transfer Switch (ATS) additionally manage the incoming power from the main grid and can start the backup generator when they detect a power outage.
Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS)
UPS is a power storage device that cleans your power supply or takes over in the event of a power failure, giving you time to switch to your backup generators if the outage is expected to last more than some short period of time (like a minute or two, depending on your UPS’s capacity).
UPS employs a power inverter to convert its stored DC power to AC current so all components in TDC can be kept running.
When a power outage hits, the UPS employs a power inverter to convert its stored DC power to AC current so all components in TDC can be kept running.
Cooling Unit
Cooling is the most integral part of a Data Center. A huge amount of power is used to keep the temperature under check for the machines to stay healthy.
Having an excess of warm air and humidity within your data center can lead to overheating of high-end CPUs that generate an immense amount of heat when in action. If this heat is not controlled, the machines will get too hot and shut down or crash.
Today, there are various techniques used by different data centers across the world
Pumped Refrigerant
Indirect Air Evaporative System
Chilled Water System
Containment
Power Distribution Unit (PDU)
PDU are the extensions or power outlets where the equipment are plugged in Each PDU contains several points where the equipment can be plugged in.
The PDU receives power from UPS and it runs at 30amp/280Volts. It can handle up to 30 x 208 = 6,240 Watts. Yes, that is the general calculation to measure the total usable power. However, the safety zone recommends only 80% of the actual which comes to 4992Watts.
Equipment
These are the real heroes that actually runs the show at the Data Centers.
Equipment is nothing but your servers that incorporate Processors, Memory, Storage devices, communication equipment (Router/Switch), cables, etc.
Most of the power is consumed by the CPU/GPU where the actual processing is done. They are the heart or rather the brains of the server which does all the logical calculations.
So, these were some of the important areas where the power is used/distributed in the Data Center. However, there are few more important sections that require power usage such as
Lightings
Fire monitoring system
Alarm Systems
Security
Data center architectures and requirements can differ significantly. Regardless of classification, an effective data center operation is achieved through a balanced investment in the facility and equipment housed.