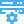
Power distribution inside Data Center
Publisher: Psychz Networks, August 01,2018In our other related articles on Data Center, we have discussed how Power functions and is distributed internally. In the following article, we will talk about how the power is transferred from one system to another in chronological order.
- Main Switch
- Automated Transfer Switch
- Uninterrupted Power Supply
- Power Distribution Unit
- Branch Circuit Monitoring
A data center is a facility housing many networked computers that work together to process, store, and share data. With the help of Data Center, we can improve usability and reduce costs related to storage, bandwidth, and other networking components.
MSB (Main Switchboard)
The supply of power at a Data Center starts with the source which is connected to the main grid, which could be provided by the power supply company. In some of the Tier 4 Data Centers, there are usually two local companies supplying the power to reduce the risk of downtime should one sector fail. This power then is connected to the main HV/LV (high voltage/low voltage) switchboard in the facility. This switchboard will provide power feeds to other distribution units like circuit breakers, etc. Each Switchboard will normally have an isolator and ways into which rated circuit breakers can be provided for individual power feeds.
Automated Transfer Switch (ATS)
Automated Transfer Switch (ATS) which are basically panels that house fuses, circuit breakers, and ground leakage protection units, take the low-voltage electricity and distribute it to Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS) system and other external entities like the cooling units. Automated Transfer Switch (ATS) additionally manage the incoming power from the main grid and can start the backup generator when they detect a power outage.
Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS)
UPS is a power storage device that cleans your power supply or takes over in the event of a power failure, giving you time to switch to your backup generators if the outage is expected to last more than some short period of time (like a minute or two, depending on your UPS’s capacity).
UPS employs a power inverter to convert its stored DC power to AC current so all components in TDC can be kept running.
When a power outage hits, the UPS employs a power inverter to convert its stored DC power to AC current so all components in TDC can be kept running.
Power Distribution Unit(PDU)
PDU are the extensions or power outlets where the equipment are plugged in Each PDU contains several points where the equipment can be plugged in.
The PDU receives power from UPS and it runs at 30amp/280Volts. It can handle up to 30 x 208 = 6,240 Watts. Yes, that is the general calculation to measure the total usable power. However, the safety zone recommends only 80% of the actual which comes to 4992Watts.
Branch Circuit Monitoring(BCM)
Branch circuit monitoring can be done on individual circuits especially when you want to monitor the usage.
This way you can separate different devices or users and keep a check on each.
Using a Circuit metering users can meter multiple circuits together in a close proximity. This form of metering offers a refined, granular view of how energy is consumed over multiple circuits in a home or building.