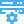
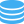
Access Logs Download Settings
Publisher: Psychz Networks, August 15,2021Access logs provide you the data required to analyze your daily traffic patterns and also to view the frequency of certain visitors. You can choose to download the reports based on various available filters. Download Settings help you to choose (Add or Delete) filters that you want under your report.
Adding Parameter (to the column)
From the drop-down menu of the "Download Columns", you can select and add the parameter (as a column) to your report which you can download.
Moving the Parameter (within the columns)
Once you add the parameters, you can view them below in the row format. You can choose the parameter that you would like to move up or down depending on the sequence you want and use the Up and Down arrow buttons to move.
Deleting the Parameter
Select the parameter you would like to delete and click on the red cross button on the right of the selected parameter.
Following are the available filters and their uses
Request Time: The number of milliseconds the request was in flight from the server's
perspective. This value is measured from the time your request is received to the time
that the last byte of the response is sent.
URL: URL to which the request was made. The Request-URI part of the HTTP request message.
Connection: Network Connection means an Internet access service for use by multiple machines
Connection Request: Connection request urges your proxy to establish an HTTP tunnel to the
remote end-point.
Content Length: The Content-Length header indicates the size of the message body, in bytes,
sent to the recipient.
Body Bytes Sent: The amount of data sent through the interface to a client
GZip Ratio: Web servers use gzip as compression method to reduce the total amount of data
transferred to clients. GZip offers a range of compression levels from 1 to 9.
HTTP Header Name: HTTP headers let the client and the server pass additional information
with an HTTP request or response. An HTTP header consists of its case-insensitive
name followed by a colon (:), then by its value.
Server Address: The web server address is an external IP address that connects your computer
to the Internet Service Provider (ISP), enabling access to various domains worldwide.
The Server IP address differs from your website IP address. You shouldn't use it as
an A record when you're setting up DNS for your domain.
Remote User: The apparent internet address of the requester. Intermediate proxies and
firewalls might obscure the actual address of the machine making the request.
HTTP Reference: The HTTP Reference is an optional HTTP header field that identifies the
address of the webpage (i.e., the URI or IRI), which is linked to the resource being
requested. By checking the referrer, the new webpage can see where the request originated.
HTTP User Agent: Type of the HTTP method used by the request or connection.
Bot: Tells you if a bot is used to initiate the request. The value passed under this is
either a Yes or a No.
Mozilla Version: Mozilla Version used
Platform: A platform is any hardware or software used to host an application or service
OS : Operating system used at the request origin
Engine Name: Name of the browser engine which is a core software component of every major
web browser.
Following are the browsers and Engines they use
- Google Chrome and Opera v. 15+: Blink
- Internet Explorer: Trident
- Mozilla Firefox: Gecko
- Chrome for iOS and Safari: WebKit
Engine Version: Engine Version used
Browser Name: browser used to generate the request
X Proxy Cache: This field defines the cache hit/miss at the server. The fields Expires and
Cache-Control tell the browser (and all intermediate HTTP proxies) what the
lifetime of the contents is and how it can be cached.
Language: Language used
Geo IP City: The City code where the request came from.
Geo IP Country: The country code where the request came from.
Data center Name: Name of the last known Data Center in the connection, identified by its
edge server.